Some of my students express anxiety about becoming deficient in certain nutrients once they switch to a plant-based diet. All of us, of course, should always be concerned with getting sufficient nutrients, but it’s funny that these fears seem to appear only after a person has eliminated animal products. Those around us bolster these fears too. Tell someone you are vegan and the first thing you’ll be asked is where do you get your x, y or z. Tell someone you eat animals and no one is concerned (which is unfortunate because the vast majority of non-vegans do not consume nearly enough nutrients like fiber, phytochemicals, and antioxidants which, of course, can only be found in plants). The implication is that only when we go vegan do we need to be concerned with deficiency.
This is just silly. We all need to remember that there is nothing magical about flesh or dairy. They don’t contain unique properties that cannot be found elsewhere. No one, at any stage of life, needs to consume them. Period. Human beings don’t require specific ingredients; we require specific nutrients. And again, neither flesh nor dairy contains required nutrients that cannot be found elsewhere.
When kids enter the picture, this anxiety only grows both within us and from the world around us, including from doctors (which is particularly infuriating). I recently received the following inquiry from a friend: “I feel so ‘obligated’ to give my 1 year old whole milk because it’s so ingrained in my brain, but please let me know if you have any good sources of information on feeding babies soy and/or almond milk. I asked my son’s doctor, and she said to stick with whole milk. Her reasoning wasn’t very convincing though (as much as I hate to second guess her judgement).”
When kids enter the picture, this anxiety only grows both within us and from the world around us, including from doctors (which is particularly infuriating). I recently received the following inquiry from a friend: “I feel so ‘obligated’ to give my 1 year old whole milk because it’s so ingrained in my brain, but please let me know if you have any good sources of information on feeding babies soy and/or almond milk. I asked my son’s doctor, and she said to stick with whole milk. Her reasoning wasn’t very convincing though (as much as I hate to second guess her judgement).”
Stories like this make me want to pull my hair out.
First of all, I need to remind people that doctors receive almost no nutrition training in medical school. I know that sounds absurd, but unfortunately, it’s true. The advice you’ll get from most doctors isn’t worth that much more than the advice you would get from asking Joe Schmo on the street. Often times doctors will just tell their patients to do what they themselves have always done or what their parents always did. In other words, when it comes to nutrition, the advice doctors give is usually based on their own habits rather than on science. After all, doctors used to advocate smoking cigarettes to patients because they smoked cigarettes themselves!
So, do toddlers need to consume cow’s milk? The answer is NO.
In previous posts, I’ve discussed why dairy is harmful, but here’s a quick recap: Recent scientific studies have suggested that dairy products may be linked to increased risk for prostate cancer, testicular cancer, and possibly for ovarian and breast cancers. And despite the widespread myth that dairy milk is good for your bones, it has actually been singled out as the biggest cause of osteoporosis. Dairy is also high in cholesterol and saturated fat, which leads to heart disease. And over 75% of people on this planet are genetically unable to digest dairy, yet we label this near universal human trait “lactose intolerance” as if it were some disease or deficiency. Here’s the reality: Human babies are born with an enzyme that allows us to digest our mother’s milk. Between the ages of two and five, the vast majority of humans lose this enzyme because we are supposed to be weaned by then. Our bodies simply weren’t designed to be consuming milk into adulthood (let alone the breast milk of another species!). This is why so many babies and toddlers who are fed cow’s milk suffer from digestive upset. Nothing is wrong with them; it’s what they are being fed!
So why do so many pediatricians recommend feeding human babies whole cow’s milk?
Whole cow’s milk is a go-to for parents and pediatricians simply an easily accessible source of fat, calcium, and vitamin D that is readily available in supermarkets. That’s it. Again, there is nothing magical about cow’s milk for humans, whole or otherwise.
Fortunately, there are an increasing number of doctors who are starting to wake up to the nutrition science. In fact, in 2008 and 2011 the American Academy of Pediatrics published releases that discouraged the transition to whole cow’s milk because of the increased risk of cardiovascular disease. In “Disease-Proof Your Child” (which I highly recommend!), Dr. Joel Fuhrman advises against cow’s milk because it can create gastroesophageal reflux, iron deficiency, and calcium sodium excess in infants and toddlers. It also lacks DHA, a necessary ingredient for brain development. And Pediatrician Dr. Natasha Burgurt explains that “unlike the dietary needs of an infant, milk is no longer a source of complete nutrition after a child’s first birthday. Milk provides a convenient source of fat, protein, calcium, and vitamin D for growing bodes. But, in today’s average food lifestyle, these building blocks can be more than adequately supplied in other areas of a balanced diet.” In other words, toddlers can get their nutrients from food, rather than a beverage. In fact, Dr. Burgurt argues that this is preferable. “In a society that typically drinks too many unnecessary calories,” she says, “it is preferred that children develop a preference for low-fat, low-calorie, unsweetened beverages.”
The bottom line is that toddlers don’t need cow’s milk. What toddlers do need are specific nutrients. In “Becoming Vegan” (a must-have book on nutrition), Brenda Davis, RD and Vesanto Melina, MS, RD recommend breastfeeding a baby for a minimum of one year and preferably for a full two years or more. If you decide to stop breastfeeding (or using formula), “during the 12-24 month period, fortified soymilk is your best alternative. It should contain calcium, vitamin B12, and vitamin D.” They also recommend including plenty of higher-fat foods in a toddler’s diet. Some examples of foods that provide these important sources of fat include tofu, smooth nut butters, mashed avocado, soy yogurt, puddings, and moderate amounts of olive, canola, and flax oil. Omega-3 fatty acids can be found in dark green leafy vegetables, seaweeds (which are the the original source for fish), selected seeds (flax, chia, hemp), nuts (walnuts, butternuts), and soybeans. Calcium-rich foods for toddlers include breast milk, commercial soy formula, or full-fat fortified soymilk. Food sources of vitamin B12 include nutritional yeast, fortified soy and grain milks (such as Edensoy Extra, Silk, Soy Dream, Rice Dream, So Nice, and Vitasoy Enriched), fortified breakfast cereals (such as Raisin Bran, Kelloggs Cornflakes, Grapenuts, Nutrigrain, and Total). Vitamin D–which does not exist naturally in cow’s milk; it’s only there because it has been fortified–can also be found in other fortified foods, including nondairy milks, or from sufficient sun exposure.
Reed Mangles, PhD, RD provides the following chart on the Vegetarian Resource Group (as well as in her nutrition book, Simply Vegan):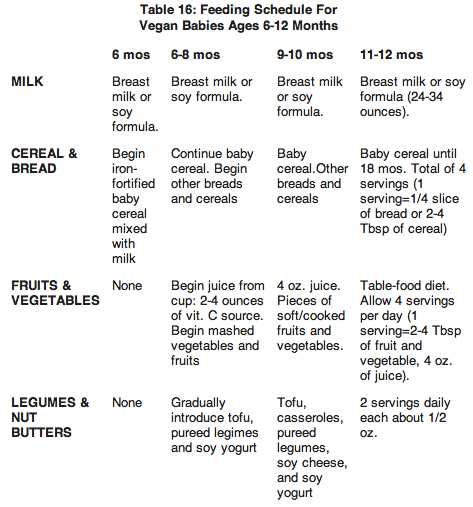
Reed Mangles, PhD, RD provides the following chart on the Vegetarian Resource Group (as well as in her nutrition book, Simply Vegan):

No one wants to give their child a beverage linked to so many health problems, and I believe that deep down we all care about the mothers and babies of other species and don’t want to cause them harm if we don’t have to. For all of you with a little one in your life, I hope this information gives you the confidence to feed your children healthfully and compassionately 🙂
Below are some links I found from vegan moms raising vegan toddlers that may be helpful:

